LANGUAGE OF LEAN
Push Principle
The Push Principle Concept/Term refers to a production system where material and products are manufactured and moved along the production line based on a predicted demand, rather than actual demand.
The Push Principle Concept/Term refers to a production system where material and products are manufactured and moved along the production line based on a predicted demand, rather than actual demand. This system operates under the assumption that the customer demand can be accurately forecasted and the production line can be appropriately scheduled to meet that demand.
However, the Push Principle often leads to negative impacts on operations. One of the main problems with this system is the assumption of accurate demand forecasting. In reality, customer demand is highly unpredictable and can fluctuate rapidly, leading to overproduction and inventory buildup. This excess inventory creates significant problems such as storage and handling costs, obsolescence, and potential quality issues.
Additionally, the Push Principle often results in an inefficient utilization of resources. The production line is designed to produce a set amount of product, regardless of actual demand. This can lead to idle time and equipment, increased energy costs, and reduced production capacity. The production process is also disrupted by production line breakdowns, worker absences, and equipment failures, resulting in increased downtime and decreased efficiency.
Another negative impact of the Push Principle is that it can lead to a lack of focus on customer needs. The emphasis is on meeting a predetermined production schedule, rather than meeting the actual needs of the customer. This can result in an overproduction of products that are not needed, as well as a lack of flexibility to adapt to changing customer demand.
To mitigate these negative impacts, Lean Management experts advocate for the implementation of the Pull Principle. The Pull Principle is a system where production is based on actual customer demand, rather than a predicted demand. This system allows for a more flexible and efficient utilization of resources, as well as a greater focus on meeting the actual needs of the customer.
In a nutshell, the Push Principle can lead to negative impacts on operations such as inventory buildup, resource inefficiency, and a lack of focus on customer needs. Lean Management experts recommend the implementation of the Pull Principle as a more efficient and effective alternative. By focusing on actual customer demand, organizations can achieve greater operational efficiency and meet the needs of their customers.
Bullwhip Effect
The bullwhip effect is a well-known phenomenon in lean management that can have a significant impact on the push and pull principles of supply chain management.
The bullwhip effect is a well-known phenomenon that can have a significant impact on the push and pull principles of supply chain management. The bullwhip effect refers to the amplification of demand fluctuations as they move up the supply chain, leading to increased inventory, increased costs, and decreased customer satisfaction.
The bullwhip effect is caused by a number of factors, including demand forecast errors, order batching, price fluctuations, and the use of incentives that encourage suppliers to order more than they need. These factors can cause suppliers to overreact to demand changes, leading to excessive inventory levels and higher costs.
The impact of the bullwhip effect on the push and pull principles of supply chain management can be significant. The push principle is based on the idea that suppliers produce goods based on demand forecasts, and then push the goods to the customer. The bullwhip effect can cause demand forecasts to become less accurate, leading to increased inventory levels, increased costs, and decreased customer satisfaction.
The pull principle, on the other hand, is based on the idea that suppliers produce goods based on actual customer demand. The bullwhip effect can cause suppliers to overreact to demand changes, leading to increased inventory levels and higher costs. This can result in a situation where suppliers are producing goods that are not actually needed, leading to a decrease in customer satisfaction and increased waste.
To address the bullwhip effect, organizations can implement a number of strategies, including improving demand forecasting accuracy, reducing order batching, reducing price fluctuations, and using incentives that encourage suppliers to order what they need, when they need it.
One approach to reducing the bullwhip effect is to implement a demand-driven supply chain management system. This involves using real-time data to better understand customer demand, and using this information to make informed decisions about inventory levels and production schedules. This can help to reduce the bullwhip effect, leading to more accurate demand forecasts, lower inventory levels, and increased customer satisfaction.
Another strategy to address the bullwhip effect is to implement a lean supply chain management system. This involves reducing waste, streamlining processes, and improving communication and collaboration between suppliers, manufacturers, and customers. This can help to reduce the bullwhip effect, leading to improved supply chain efficiency, lower costs, and increased customer satisfaction.
In a nutshell, the bullwhip effect is a well-known phenomenon in lean management that can have a significant impact on the push and pull principles of supply chain management. To address the bullwhip effect, organizations can implement a number of strategies, including improving demand forecasting accuracy, reducing order batching, reducing price fluctuations, and using incentives that encourage suppliers to order what they need, when they need it. By implementing these strategies, organizations can reduce the bullwhip effect, leading to more accurate demand forecasts, lower inventory levels, and increased customer satisfaction.
JIT
Just-in-Time (JIT) is a manufacturing and inventory control system in which raw materials, components, and finished products are delivered to the production line exactly when they are needed.
Just-in-Time (JIT) is a manufacturing and inventory control system in which raw materials, components, and finished products are delivered to the production line exactly when they are needed. The goal of JIT is to minimize inventory levels and reduce lead times, while maintaining high levels of production efficiency.
JIT is a pull-based system, which means that production is driven by customer demand rather than by a production schedule. This is achieved by using Kanban, a signaling system that alerts the supplier to send more materials or components when the inventory level of a specific item reaches a predetermined minimum level.
The origins of JIT can be traced back to the manufacturing practices of the Toyota Motor Company in the 1950s. It was developed by Taiichi Ohno, an engineer at Toyota, as a response to the inefficiencies he observed in the company's production processes. Ohno recognized that by reducing the amount of inventory and increasing the flow of materials, Toyota could improve its production efficiency and responsiveness to customer demand.
One of the key principles of JIT is the elimination of waste, or "muda" in Japanese. Ohno identified seven types of waste in manufacturing: overproduction, waiting, unnecessary motion, overprocessing, defects, excess inventory, and unused human potential. JIT aims to eliminate these forms of waste by creating a smooth and efficient flow of materials and products through the production process.
JIT also relies on the concept of "one piece flow", which is the production of one item at a time, rather than producing large batches of items. This allows for better control of the production process, as well as the ability to quickly identify and correct any problems that may arise.
Another important aspect of JIT is the use of visual management tools, such as Andon boards and Kanban boards. These tools allow for real-time monitoring of the production process, and can alert workers to potential problems before they become major issues.
JIT also requires a high level of collaboration and communication between suppliers, manufacturers, and customers. This is necessary to ensure that materials and components are delivered to the production line exactly when they are needed, and that finished products are delivered to customers in a timely manner.
JIT has a number of benefits for manufacturers. One of the most significant is that it can help to reduce inventory levels, which can free up valuable floor space, reduce storage costs, and minimize the risk of stockouts. JIT can also help to improve production efficiency by reducing lead times and minimizing downtime caused by waiting for materials or components.
JIT can also help to improve product quality by reducing defects, and increasing the ability to quickly identify and correct any problems that may arise in the production process.
JIT also helps companies to be more responsive to customer demand by reducing lead times and increasing the speed of delivery. This can help to improve customer satisfaction, and increase the chances of repeat business.
JIT also helps companies to be more flexible and adaptable to changes in customer demand. It allows companies to more easily shift production to different products or product lines, which can help to maintain profitability during periods of slow sales.
However, it's worth noting that JIT is not suitable for all industries and companies, it's best applied in companies where the production process is well-defined, the demand is stable and predictable, and the lead times are short. Implementing JIT can also be challenging and requires a significant investment of time and resources to establish an effective system.
Additionally, JIT requires a high level of coordination and communication with suppliers and customers, which can be difficult to achieve. This is particularly true for companies that have a large number of suppliers or customers, or those that operate in
Kaikaku
Kaikaku first creates the basics to later carry the Kaizen idea into manual production with CIP.
KAIKAKU, which means "radical change" or "revolution" in Japanese, is a key concept in Lean management and operational excellence. It refers to a transformative approach to process improvement that aims to achieve significant and lasting improvements in performance. KAIKAKU is different from other process improvement methods, such as Kaizen, which focus on incremental improvements, KAIKAKU is characterized by a bold, dramatic change in the way a process is performed.
One of the key features of KAIKAKU is that it is not just about improving the existing process, but also about rethinking and redesigning the process from scratch. This approach allows organizations to identify and eliminate sources of waste, inefficiencies, and bottlenecks that may have been present in the process for years. By starting with a blank slate, organizations can create a new process that is more efficient, effective, and sustainable.
KAIKAKU is often used in manufacturing and production processes, where significant improvements in performance can have a major impact on the bottom line. For example, a manufacturing facility might use KAIKAKU to redesign its production process, eliminating bottlenecks, reducing waste, and increasing capacity. This could result in faster turnaround times, higher quality products, and lower costs.
Another key feature of KAIKAKU is that it often involves the use of new technologies and automation. By adopting new technologies and automating processes, organizations can achieve significant improvements in performance. For example, a manufacturing facility might use KAIKAKU to introduce robots, automated inspection systems, or artificial intelligence to its production process. This could result in faster turnaround times, higher quality products, and lower costs.
KAIKAKU also involves the active participation of employees, especially those who are directly involved in the process. By involving employees in the process improvement process, organizations can tap into their expertise and knowledge, and create a sense of ownership and engagement. Employees can also bring valuable insights into the process and suggest new ideas for improvement.
KAIKAKU is also closely linked to the concept of "Just-in-Time" (JIT) manufacturing. JIT is a production strategy that aims to produce the right products at the right time, and in the right quantities, by minimizing waste and unnecessary inventory. By implementing KAIKAKU, organizations can achieve significant improvements in performance and implement JIT successfully.
In a nutshell, KAIKAKU is a powerful method for organizations that are committed to operational excellence and continuous improvement. By rethinking and redesigning the process from scratch, organizations can identify and eliminate sources of waste, inefficiencies, and bottlenecks that may have been present in the process for years. By adopting new technologies and automating processes, organizations can achieve significant improvements in performance. By involving employees in the process improvement process, organizations can tap into their expertise and knowledge. By implementing KAIKAKU, organizations can achieve significant improvements in performance and implement JIT successfully.
KOSU
KOSU, short for "Key Operating System Units", is a method used in Lean management and operational excellence to identify and measure the critical units of a process that are essential for the overall performance and success of the operation.
KOSU, short for "Key Operating System Units", is a method used in Lean management and operational excellence to identify and measure the critical units of a process that are essential for the overall performance and success of the operation. By identifying these key units, organizations can focus their improvement efforts on the areas that will have the greatest impact on performance.
The basic idea behind KOSU is to identify the critical units of a process that are essential for the overall performance and success of the operation. This can include things like machines, equipment, personnel, and processes. By identifying these key units, organizations can focus their improvement efforts on the areas that will have the greatest impact on performance.
One of the key benefits of using KOSU is that it helps organizations to identify and prioritize the areas of the process that are most critical to performance. By identifying the key units of a process, organizations can focus their improvement efforts on those areas that will have the greatest impact on performance. This allows them to make the most of their resources and achieve the greatest return on investment.
Another benefit of using KOSU is that it helps organizations to identify and eliminate bottlenecks in the process. By identifying the key units of a process, organizations can identify which units are causing delays and bottlenecks in the process, and then take action to eliminate those bottlenecks. This can include things like improving machine maintenance, optimizing production processes, or identifying areas where automation can be used to improve efficiency.
Using KOSU also helps organizations to identify areas where standardization can be used to improve a process. By identifying the key units of a process, organizations can identify which units are taking longer than they should, and then take action to standardize those processes. This can include things like implementing best practices, developing standard operating procedures, or identifying areas where automation can be used to improve efficiency.
In addition, KOSU can be used to identify areas where automation can be used to improve efficiency. By identifying the key units of a process, organizations can identify which units are taking longer than they should, and then take action to automate those processes. This can include things like using robotics, using automated inspection systems, or using artificial intelligence to optimize production processes.
KOSU also plays a critical role in analyzing machine’s capacity. By identifying the key units of a process, organizations can identify which units are operating at full capacity, and which ones have room for improvement. This can help organizations to optimize their production processes, and ultimately, increase their overall production capacity.
In a nutshell, KOSU is a powerful method for organizations that are committed to operational excellence and continuous improvement. By identifying the key units of a process, organizations can focus their improvement efforts on the areas that will have the greatest impact on performance, eliminate bottlenecks in the process, use standardization to improve a process, use automation to improve efficiency and increase their overall production capacity.
Machine Cycle Time
Machine cycle time is a term used to describe the amount of time it takes for a machine to complete one full cycle of operation.
Machine Cycle Time is a term used to describe the amount of time it takes for a machine to complete one full cycle of operation. In the context of Lean management and operational excellence, machine cycle time is a critical metric that can be used to measure the efficiency and effectiveness of a manufacturing or production process.
The basic idea behind machine cycle time is that it measures the amount of time it takes for a machine to complete a specific task or series of tasks. This can include things like setting up a machine, loading raw materials, running a production process, and unloading finished products. By measuring the amount of time it takes for a machine to complete a full cycle of operation, organizations can gain insight into how efficiently the machine is running and identify areas for improvement.
One of the key benefits of measuring machine cycle time is that it can help organizations to identify bottlenecks and delays in the production process. By measuring the amount of time it takes for a machine to complete a full cycle of operation, organizations can identify which machines or processes are taking longer than they should, and then take action to address these bottlenecks. This can include things like improving machine maintenance, optimizing production processes, or identifying areas where automation can be used to improve efficiency.
Another benefit of measuring machine cycle time is that it can help organizations to identify areas where standardization can be used to improve a process. By measuring the amount of time it takes for a machine to complete a full cycle of operation, organizations can identify which machines or processes are taking longer than they should, and then take action to standardize those processes. This can include things like implementing best practices, developing standard operating procedures, or identifying areas where automation can be used to improve efficiency.
Measuring machine cycle time can also help organizations to identify areas where automation can be used to improve efficiency. By measuring the amount of time it takes for a machine to complete a full cycle of operation, organizations can identify which machines or processes are taking longer than they should, and then take action to automate those processes. This can include things like using robotics, using automated inspection systems, or using artificial intelligence to optimize production processes.
Machine cycle time also plays a critical role in analyzing machine’s capacity. By measuring the amount of time it takes for a machine to complete a full cycle of operation, organizations can identify which machines are operating at full capacity, and which ones have room for improvement. This can help organizations to optimize their production processes, and ultimately, increase their overall production capacity.
In conclusion, machine cycle time is a critical metric that can be used to measure the efficiency and effectiveness of a manufacturing or production process. By measuring the amount of time it takes for a machine to complete a full cycle of operation, organizations can gain insight into how efficiently the machine is running, identify bottlenecks and delays in the production process, identify areas where standardization can be used to improve a process, and identify areas where automation can be used to improve efficiency. Ultimately, measuring machine cycle time is a powerful tool for organizations that are committed to operational excellence and continuous improvement.
Swim Lane Flowchart
A Swim Lane Flowchart, also known as a cross-functional flowchart, is a type of process mapping tool that is used to visually represent the flow of a process and the various roles and responsibilities involved in that process.
A Swim Lane Flowchart, also known as a cross-functional flowchart, is a type of process mapping tool that is used to visually represent the flow of a process and the various roles and responsibilities involved in that process. The methodology of the Swim Lane Flowchart comes from the field of Lean management and operational excellence, which emphasizes the importance of efficiency and continuous improvement in business operations.
The Swim Lane Flowchart is used to clearly identify and document the steps in a process, as well as the individuals or groups responsible for each step. This allows for a clear understanding of the process and helps to identify areas for improvement. The Swim Lane Flowchart is particularly useful for identifying bottlenecks and delays in a process, as well as for identifying areas where multiple teams or departments are involved in a single process.
One of the key benefits of the Swim Lane Flowchart is that it helps to break down silos and promote cross-functional collaboration. By clearly documenting the roles and responsibilities of different teams and departments, the Swim Lane Flowchart helps to identify areas where different teams can work together more effectively. This can lead to increased efficiency and improved communication among different teams and departments.
Another benefit of the Swim Lane Flowchart is that it helps to identify areas where automation can be used to streamline a process. By clearly documenting the steps in a process and the individuals or groups responsible for each step, the Swim Lane Flowchart can help to identify areas where automation can be used to reduce human error and improve efficiency.
The Swim Lane Flowchart is also useful for identifying areas where standardization can be used to improve a process. By clearly documenting the steps in a process and the individuals or groups responsible for each step, the sSwim Lane Flowchart can help to identify areas where standardization can be used to reduce variation and improve the overall quality of a process.
In conclusion, the Swim Lane Flowchart is a powerful tool for improving business operations and promoting cross-functional collaboration. By clearly documenting the steps in a process and the individuals or groups responsible for each step, the Swim Lane Flowchart can help organizations to identify areas for improvement and take action to improve efficiency and effectiveness. Whether it is used to identify bottlenecks and delays in a process, or to promote automation and standardization, the Swim Lane Flowchart is a valuable tool for organizations that are committed to operational excellence and continuous improvement.
Standard Layout
A standard layout is a detailed, visual representation of the ideal workflow and arrangement of resources in a given area.
Standard Layout: The Key to Unlocking Efficiency in Lean Management
Standardization is one of the fundamental principles of lean management, and it's no surprise that it's also one of the most effective ways to improve efficiency and reduce waste in your operations. One of the most powerful tools in the standardization toolbox is the standard layout, also known as "taikyō-sei" in Japanese.
A standard layout is a detailed, visual representation of the ideal workflow and arrangement of resources in a given area. This can include anything from the placement of tools and equipment to the flow of materials and the location of workstations. The goal is to create a clear and consistent way of working that minimizes waste, maximizes efficiency, and makes it easy for everyone on the team to understand and follow.
One of the most important benefits of a standard layout is that it makes it much easier to identify and eliminate sources of waste and inefficiency. By clearly defining the ideal way of working, it becomes much easier to see where things are going wrong and to make adjustments as needed. This can include anything from adjusting the location of workstations to the flow of materials, to the type and size of tools and equipment.
Another key benefit of a standard layout is that it makes it much easier to train new employees and to ensure that everyone is following the same processes. When everyone is working in the same way, it becomes much easier to share knowledge and best practices, which can help to improve the overall performance of the team.
Finally, a standard layout can also be a powerful tool for continuous improvement. By clearly defining the ideal way of working, it becomes much easier to measure performance and to identify areas for improvement. This can include anything from adjusting the flow of materials to the location of workstations, to the type and size of tools and equipment.
So, how do you go about creating a standard layout? The first step is to conduct a thorough analysis of your current operations. This should include a detailed study of the flow of materials, the location of workstations, and the type and size of tools and equipment. You should also pay close attention to the flow of people and information, as this can have a big impact on overall efficiency.
Once you have a good understanding of your current operations, you can then begin to create a detailed, visual representation of the ideal workflow and arrangement of resources. This should include everything from the placement of tools and equipment to the flow of materials and the location of workstations.
It's also important to involve your entire team in the process of creating a standard layout. This will help to ensure that everyone is on board with the changes and that everyone understands the benefits of standardization.
Once you have a standard layout in place, it's important to monitor and measure its effectiveness on a regular basis. This can include anything from tracking the flow of materials to the location of workstations, to the type and size of tools and equipment. It's also important to involve your entire team in the process of monitoring and measuring performance, as this will help to ensure that everyone is committed to continuous improvement.
In conclusion, a standard layout is a powerful tool for unlocking efficiency in lean management. By clearly defining the ideal way of working, it becomes much easier to see where things are going wrong and to make adjustments as needed. This can include anything from adjusting the flow of materials to the location of workstations, to the type and size of tools and equipment. Furthermore, it is a powerful tool for training, knowledge sharing, and continuous improvement. If you're looking to improve efficiency and reduce waste in your operations, a standard layout is definitely worth considering.
Mura
A traditional general Japanese term for unevenness. It is the waste of variation in the production process.
Mura, one of the three types of waste in the Toyota Production System, translates to "unevenness" or "inconsistency" in English. It refers to the irregularity in the flow of work, causing fluctuations in capacity and production. Identifying and removing Mura is essential for creating a steady work pace and optimizing resources.
One of the main causes of Mura is multitasking. When team members are constantly switching between tasks, they often lose focus and efficiency, leading to unevenness in the workflow. This results in longer lead times, increased inventory, and higher costs.
Another cause of Mura is overproduction. Producing more than what is needed, whether it's goods or services, creates an imbalance in the system and results in unnecessary inventory. This not only ties up valuable resources but also increases the risk of defects and rework.
To handle Mura, one must first understand the root cause of the unevenness. This can be done through value stream mapping, a tool that visually represents the flow of work and helps identify areas of waste. By analyzing the current state of the process, one can identify the steps that are causing Mura and implement solutions to eliminate them.
One effective solution is to implement a pull system, also known as "kanban" in Japanese. This system ensures that work is only produced when it is needed, eliminating overproduction and promoting a steady flow of work.
Another solution is to implement standard work. By standardizing the work process, team members are able to work consistently and efficiently, resulting in less Mura. This also helps in identifying and addressing any abnormalities that may occur in the process.
Additionally, involving the team members in problem-solving and continuous improvement activities can lead to increased ownership and accountability, leading to a reduction in Mura.
Implementing a pull system, standard work and involving team members in problem-solving and continuous improvement activities can help organizations to create a steady flow of work and optimize resources.
It's important to note that Mura is not a problem that can be solved once and for all. It's a continuous effort and requires constant monitoring and improvement. Regularly conducting value stream mapping and Gemba walks, where one goes to the place where the work is done to observe and understand the process, can help in identifying and addressing Mura.
In conclusion, Mura is a key concept in lean management and must be addressed to ensure a steady work pace and optimize resources. By understanding the root cause of Mura and implementing solutions such as pull systems, standard work, and involving team members in problem-solving and continuous improvement activities, organizations can achieve the goal of smooth and well-organized workflow.
Mentor
In the world of lean, the mentor strives to improve the competencies of his / her charge and thereby improve the level of problem-solving and improvement within the organization.
The concept of mentorship can be traced back to the story of "The Odyssey" by Homer, where Mentor was a trusted advisor to Odysseus and a mentor figure to Telemachus.
Telemachus viewed him as a wise and experienced older person who guided him, offered him encouragement and support, and helped him develop into his role and responsibilities.
Lean management is a methodology that aims to eliminate waste and optimize resources in order to improve efficiency and productivity. It is widely used in various industries and has been proven to be highly effective in reducing costs, increasing quality, and improving overall performance. However, implementing lean management can be challenging, especially for those who are new to the field. This is where the role of a mentor comes in.
A mentor is a seasoned professional who has extensive experience in lean management and is willing to share their knowledge and expertise with others. The mentor's role is to guide, advise, and support the mentee in their journey to become proficient in lean management. They provide valuable insights and practical advice that can help the mentee avoid common pitfalls and achieve their goals more quickly.
One of the main benefits of having a mentor is that they can provide the mentee with a different perspective on the problems they are facing. Mentors have a wealth of experience and have likely encountered similar issues in the past. They can share their knowledge and offer solutions that the mentee may not have considered. This can be especially valuable when the mentee is dealing with a complex problem that requires a unique solution.
Another benefit of having a mentor is that they can provide guidance on how to implement lean management in a specific industry or organization. Lean management can be applied to many different types of businesses, but the specific implementation may vary depending on the industry or organization. A mentor can provide guidance on how to tailor lean management to the mentee's specific situation and help them avoid common mistakes.
Moreover, mentors can provide a sounding board for the mentee to discuss their ideas and concerns. This can be particularly beneficial when the mentee is dealing with a difficult situation or trying to navigate a complex process. Mentors can help the mentee to think through their options and make the best decision for their situation.
In addition, mentors can provide the mentee with access to a network of professionals who can offer additional support and advice. This can be especially valuable when the mentee is trying to find resources or connect with other professionals who can help them with their specific goals.
Overall, the role of a mentor in lean management is crucial. They provide guidance, support, and practical advice that can help the mentee become proficient in lean management more quickly and effectively. They offer a different perspective on problems and can provide guidance on how to implement lean management in a specific industry or organization. And they offer a sounding board and access to a network of professionals.
In a nutshell, having a mentor can make a significant difference in the mentee's ability to implement lean management successfully and achieve their goals. It is important for organizations and individuals to find a mentor who can provide the guidance and support they need to excel in their journey of implementing lean management.
Standard WIP (SWIP)
The minimum amount of material or a given product, which must be in process at any time to ensure proper flow of the operation.
The minimum amount of material or product that must be in the process at all times to ensure smooth operation.
Standard Work is a little underrated concept in Lean Manufacturing. It is not simply standardization or work standards.
Standard Work is composed of three elements: Takt time, Work sequence and Standard Work in Process (SWIP). Takt Time is a fundamental concept of Lean Manufacturing, and Work Sequence is relatively intuitive. SWIP, however, is a bit more complex.
SWIP refers to the minimum necessary in-process inventory (work in process or WIP) to maintain Standard Work. It is not more or less than what is needed. To calculate the appropriate quantity for SWIP, one must ask a number of questions.
While a rough estimate of SWIP can be obtained by using the equation SWIP = Sum of Cycle Times / Takt Time, it is still necessary to determine where exactly this SWIP should be applied. The following steps provide a guide for determining the appropriate quantity of SWIP:
what’S the team size?
Standard Work is the most efficient combination of manpower, material, and machine, and is based on takt, work sequence, and Standard Work in Process (SWIP). By definition, it should include manual work. If a process is fully automated, it is not considered Standard Work. Instead, it is likely an NC program.
To determine the appropriate team size, the sum of manual cycle time is divided by Takt Time. Therefore, one piece of SWIP per person is required. The equation for manual SWIP would than be:
SWIP(manual) = Team member x (1 piece = person)
When determining the amount of SWIP, there should be no rounding, unless there is less than a full person. In that case, round up to the nearest whole number.
process steps as automatic one-piece cycle machines
Standard Work assumes the use of multiple processes or machines, and separates human and machine tasks as much as possible.
When using an automatic cycle, the worker will only be responsible for loading and unloading, and will not be present during the actual cycle. The automatic cycle time must also be shorter than the Takt Time, ensuring that there is always at least one piece in the machine during each cycle.
This is known as SWIP (single piece auto), and is calculated as the number of single-piece automatic cycle machines multiplied by one piece per machine. There is no rounding necessary as it is not possible to have less than a full machine. However, this only applies to single-piece automatic cycles, and calculations for batch processes or cycles with longer lead times may differ.
process steps as a single-piece non-machine automatic cycle
The term "non-machine automatic cycle" refers to process steps such as the drying time for paint, curing time for epoxy, and cooling time for hot parts.
These process steps may not involve machines, but they do require a certain amount of time for completion. The ratio of this time to the Takt Time is known as the Single-Piece Non-Machine Automatic (SWIP) cycle.
It is important to note that this value should always be rounded up to the nearest whole number. In some cases, equipment like turn tables or FIFO racks may be used to manage the curing process, ensuring that a finished product is available for each takt, and a new one is added for curing.
Process steps with a batch automatic cycle
Batch processes refer to situations in which equipment is designed to unload and load multiple pieces at a time, rather than one piece at a time.
A common example is heat treatment processes where a vacuum must be maintained and the door cannot be opened for hours. In such cases, a batch of parts is removed and then another batch is loaded. The cycle time per piece may be less than the Takt Time, but the overall automatic Cycle Time is greater than the Takt Time.
The Single-Piece Non-Machine Automatic (SWIP) cycle in this case is calculated as (Automatic time / Takt Time) x 2. The reason for this is that in batch processes, which do not allow for the addition or removal of individual pieces during the Takt, an extra quantity of complete parts is required. This concept can be compared to the idea of a pulley and bucket system used to retrieve water from a well, where one bucket is at the bottom of the well, full of water and another bucket is at the top, full of water, and during Takt, you empty out the bucket one by one and fill it back up one by one.
It's worth noting that in formulas 2, 3 and 4, manual cycle time is not included in the calculation because rule #1 takes care of that. This is because every manual Cycle Time must be within Takt by definition of Standard Work and since the unload/load time will involve one piece, there is no need to add manual time back into the calculation (in most of the cases).
Muri
Muri, a Japanese term meaning "unreasonable, impossible, or overburdened," refers to the excessive demands placed on resources, such as equipment and operators, which can lead to wear and production downtime.
Muri, a Japanese term meaning "unreasonable, impossible, or overburdened," refers to the excessive demands placed on resources, such as equipment and operators, which can lead to wear and production downtime. This traditional Japanese concept is often associated with overburden, unreasonableness, and absurdity. However, it can be eliminated through the implementation of standard work practices.
INTRODUCTION
Lean management aims to optimize resources and eliminate wasteful activities in the production process. However, many lean practitioners often focus solely on identifying and eliminating the 7 wastes, known as Muda, neglecting the importance of the other two M's: Mura and Muri.
Identifying and addressing Mura (unevenness) is essential for creating a steady work pace, but it is equally important to identify and address Muri, which is the overburden of resources in the organization's work system. By identifying Muri, organizations can analyze and optimize the capacity of their workforce.
Let's dive deeper into understanding what Muri is and its significance.
What does Muri stand for?
As a lean expert, it's important to understand the concept of Muri, which is a Japanese term meaning "overburden or unreasonable." It is one of the three types of waste (Muda, Mura, Muri) and a key element in the Toyota Production System.
Muri occurs when demands placed on a team exceed their capacity, leading to stress and decreased productivity and efficiency. This can also result in extra working hours and occupational burnouts, negatively impacting team morale and the overall health of the work process.
To avoid this, it's important to be mindful of the workload and to strive for balance at the optimal capacity, where all parts of the system are able to deliver results without the need for extra work. It's also essential to understand the root causes of Muri in order to effectively address it.
What can Muri cause?
It's important to be aware that overburdening teams can occur without conscious intent. Setting unrealistic deadlines, for example, can lead team members to rush their work and result in poor quality and decreased customer satisfaction.
For instance, if a designer is asked to create twice the number of images they are capable of producing within a certain timeframe, it's likely that the final output will not be of the highest quality.
This analogy can be applied to an assembly line as well, where rushing the process can increase the likelihood of low-quality products being delivered to customers. There are various reasons that can contribute to creating Muri and it's important to identify and address them to maintain a smooth and efficient workflow.
Over-demanding
One of the most apparent causes of Muri is over-demanding, where higher management places excessive workloads on teams with the belief that more inputs will result in more outputs.
However, this often leads to a rising number of pending tasks and can cause chaos and burnouts among the team members. This over-demanding behavior is commonly seen in the contemporary business world, it is important for management to be aware of the consequences of overburdening the team, and to instead aim for a balance between inputs and outputs.
Lack of training
The lack of proper training can lead to inefficiencies and the prolonging of tasks. For example, if a team member is not properly trained for a specific task, they may take longer to complete it than necessary.
For instance, if an individual is trained as a copywriter but is assigned tasks of a designer, they may require twice as much time to produce high-quality images as compared to a regular designer who is properly trained for that role.
This highlights the importance of providing proper training and ensuring team members are equipped with the necessary skills to perform their roles effectively, which can help prevent Muri and optimize the workflow.
Lack of communication
Effective communication is crucial for the success of any team. To avoid overburdening, it is essential to establish clear communication channels and practices.
For example, if a meeting with team members is held and a decision is made to create 10 new landing pages for a website, it is important that all team members are informed and aware of the project, including the expected deadline.
Failure to do so, such as in the scenario where a designer is not informed until the last day before the deadline, can lead to overburdening and negative consequences of Muri due to miscommunication. Clear communication can prevent such situations and help teams work efficiently and effectively.
Lack of proper tools and equipment
When the necessary tools and resources are absent, the occurrence of Muri becomes evident and unavoidable. For example, if certain developers are given new computers while others are still using outdated equipment, the latter group will experience overburdening as they will require more time to complete their tasks.
Muri can be caused by various factors, it's important to keep in mind that managing and addressing all of them is crucial in order to maintain a stable and efficient workflow.
To effectively deal with Muri, it's important to identify and understand the root causes, and develop strategies to address them. This may include providing proper tools and resources, implementing clear communication channels, and providing adequate training to ensure that teams have the necessary skills to perform their roles effectively.
Different ways to deal with Muri
Lean management offers various techniques and strategies that can assist in minimizing the negative impact of overburdening or eliminating it altogether.
Map your team’s workflow
A useful starting point in identifying and addressing Muri is to map out your team's workflow. One tool that can aid in this process is a Kanban board, which visually displays the various stages of the workflow and allows for an understanding of your team's capacity and where value is added.
Next, implementing work-in-progress limits for each stage of the workflow can ensure that team members are not juggling multiple tasks at once, but are focusing on completing one task before moving on to the next. This helps to create an efficient pull system, which leads to better organization and prevents overburdening.
When dealing with multiple teams whose work is interdependent, it is important to also implement WIP limits on a global level. For example, if team A is responsible for developing new features for a software service and team B is responsible for deploying those features, but team A is delivering new features faster than team B can deploy them, team B will be constantly overburdened. To avoid this, team A must ensure that team B has the capacity to handle new features before starting work on them. This may mean that team A may have to wait, but it is better to have one team blocked than have the entire company impacted.
Standardize your process
Another approach to addressing Muri is through the implementation of standardization. By documenting all processes and providing thorough training to team members, you can ensure that everyone is equipped to complete their tasks in an efficient and effective manner. This promotes clear communication and helps to eliminate misunderstandings, which can contribute to overburden.
Practice Jidoka
Another Lean management technique that can be used to address Muri is Jidoka. This practice empowers team members to halt the work process if an issue arises, and requires the problem to be resolved before the process can continue. This helps to establish built-in quality standards and prevent the need for rework.
Furthermore, regularly conducting Gemba walks, which involve physically going to the work area to observe and understand what is happening, can also provide insight into where Muri is occurring and how it can be addressed.
In a nutshell
Many businesses unknowingly put excessive demands on their staff, known as Muri in Japanese. This can lead to decreased efficiency and wasted resources, impacting profitability. To address Muri, it is important to:
Provide proper training and necessary tools and equipment to teams
Establish clear communication channels and protocols
Implement standard procedures within the organization
Standard Work Combination Sheet
In lean management, a standard work combination sheet is a document that displays the process steps for one or several employees. It is used to show the optimal combination of human and machine work.
In lean management, a standard work combination sheet is a document that displays the process steps for one or several employees. It is used to show the optimal combination of human and machine work. The sheet includes information on the timing values between different steps of the process, including manual work time, walk time, and machine processing time. The data recorded on the sheet is analyzed to identify any significant waste or delays in the process, and can be used to help determine the direction the company needs to take to address these issues. The sheet can also be used to evaluate the performance of individual employees, such as identifying if someone is overburdened with tasks or underutilized. Let’s go in a little bit detail in the following.
Standardized Work Combination Sheet
A Standardized Work Combination Sheet is a document that provides an overview of the interactions and timing between different parts of the work process. It displays how the various timing values such as manual work time, walk time, and machine processing time, combine and interact with each other. The sheet is designed to capture key data that is relevant to the understanding of the workflow and timing of the process.
What you should record
The data for each individual operator working on the floor is recorded in the Combination Sheet, and then analyzed using various forms of analysis. This sheet is useful for identifying any significant waste in delays between separate process steps, and can provide a clear indication of the direction the company needs to take to address these issues.
The most important points recorded in the sheet are the time required for human and machine movement, all based on the Takt Time. The sheet can help the company quantitatively evaluate an individual worker's performance and identify if they are overburdened by their current tasks.
Additionally, it can also reveal if a particular employee could be utilized more effectively. Often, companies may not realize that one of their workers is underutilized, spending less time performing actual work than expected. By properly recording and analyzing data using relevant tools to standardize the working environment, all the information will be easily accessible.
Eliminate waste
The Combination Sheet can help identify and eliminate waste in the production process by observing data recorded on the sheet, such as the time operators spend waiting for machines to complete tasks, waiting for input from other machines, or waiting for other operators to perform their tasks.
While some waiting may be necessary and an inherent part of the work process, it can be challenging to distinguish between necessary and unnecessary downtime. The Combination Sheet provides a comprehensive understanding of the current state of the production process and an objective view of each individual's involvement.
The data collected from the sheet is well-suited for graphical representation and can be easily analyzed using visualization tools. It may be incorporated into the sheet itself or handled by another department. The most crucial aspect is that the data is collected and organized correctly, as it can always be processed later.
How accurate should it be
The level of precision required for timing measurements can vary depending on the nature of your organizations processes. In some cases, it may not be necessary to record times down to the last second, such as when processes typically take over ten minutes. On the other hand, if the organization relies on many small and fast-paced processes, it may be necessary to use external devices to measure time as it would be difficult for a human operator to keep up.
It is essential to ensure that all data is measured consistently, as this is what establishes the validity of the data for later analysis. It is not advisable to round off one part of the data set while keeping another precise as it can lead to statistical deviations that are challenging to explain.
So what does it mean?
Employees may initially be uncertain about their new responsibilities related to completing the Combination Sheet, but taking the time to provide guidance and training can lead to significant improvements in the overall efficiency of the organization. Standard work can bring about significant changes in a company, but it is important to be patient and provide clear instructions during the initial implementation process. It can be a challenging transition, which is why it is essential to be well-versed in all the tools and techniques involved.
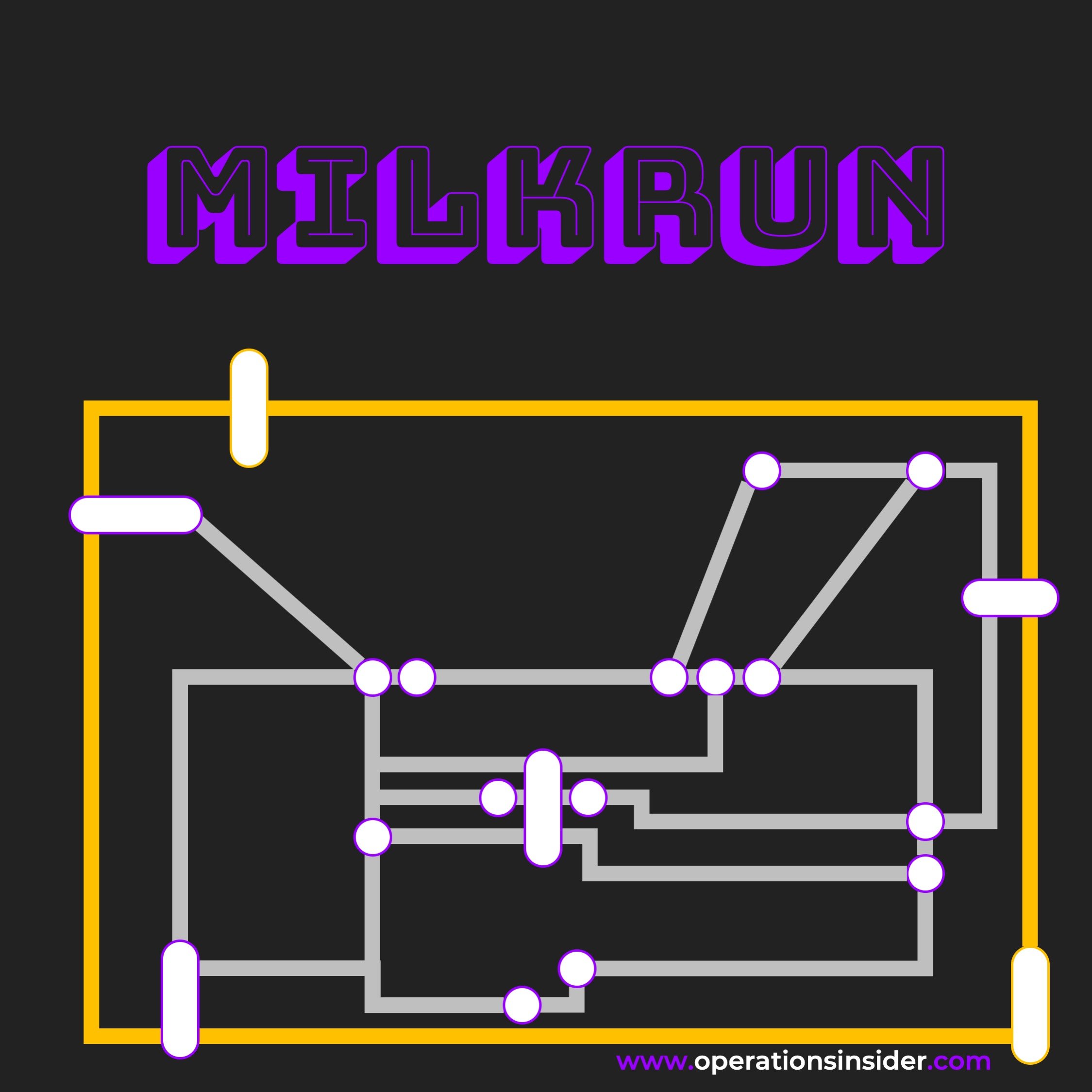
Milkrun
The Milkrun is the preset intralogistics concept to bring raw material, semi finished and finished goods to the place they belong at the time they are needed.
The Milkrun is the preset intralogistics concept to bring raw material, semi finished and finished goods to the place they belong at the time they are needed. The Mikrun is implemented based on existing consumption values, an internal supply cycle is defined in which deliveries on fixed routes are installed with specific times.
Based on these current consumption values, a logistic supply cycle is defined wherein raw material, semi and finished goods are delivered and picked up by a fixed route at a specific time. With this you will also optimize your intralogistics concept in general taking on action for a Milkrun concept.
So what is the idea behind the Milkrun concept.
The term Milkrun comes from the traditional milkman that was supplying milk to homes on a fixed route in a specific time. The milk delivery was based on the consumption of the households, by this only the amount of milk needed was delivered. Empty bottles have been picked up at the same time and brought back to the distribution center. So quite simple full bottle(s) delivered, empty bottle(s) picked up.
The cross company Milkrun
Nowadays the material management got a little bit more complex. Speaking in the external way of logistics a Milkrun is a supplier concept where customers ask for one or more shipping companies to manage different suppliers or customers on after the other in the form of a shipping cycle. In this way, goods and empty containers can be delivered and received at the same time without the need of centralization. The main goal is to have as less as possible empty trucks and at the same time being under full control of external material flow. Tours and deadlines are the guard rails on these cycles, reducing storage space is the nice to have side effect.
The benefits of the Milkrun concept
With installing a Milkrun you will be able to reduce shipping times, processing processes and therefore handling costs.
Just in Time and Just in Sequence deliveries are possible
Your planning is more structured as you will have fixed time frames
Less capital needed due to decreasing inventory/stock/WIP
You can integrate waste and empty container management
Increase of sustainability due to ecologically smarter transportation routes
Of course there are also some challenges with the Milkrun concept
Time consuming planning as quantity, duration, replenishment time, etc. needs to be considered
Processes and products need constant supply
Outbound Milkruns can be delayed by traffic or weather conditions
Economically relevant for larger business or higher demands of goods
Reliable supplier for products and transport needed
One last note for the internal Milkrun
Inbound the concept can be used in both ways, intralogistics and manufacturing. E.g. certain raw materials or semi-finished goods can be delivered on a regular basis to predefined workstations where the consumption can simply calculated. And on the fixed route the Mizusumashi can collect empty container and waste from production. This reduces internal ways of operators and guarantees a continuous supply of workstations. The next level would be to interlink all workstations or cells with your internal supply cycles to create an intralogistics flow, reducing the manual replenishment work. To find out what the Mizusumashi is just go here. In short: he/she is the guy who supllies goods on the shop floor in a structured process.
8D
8D Reports are used to communicate results of taken problem solving steps to the customer in a standard format.
The so called “8D”-Report is a document resulting from an 8D process which is part of a structured problem solving process in quality management if there are quality issues between customer and supplier.
8D represents the eight mandatory process steps that are performed when processing a claim to get to the root of the cause. The report details the nature of the claim, responsibilities, and actions taken to prevent the problem from reoccurring:
The 8D methodology is intended to ensure that complaints are dealt with systematically. Consistent documentation of the associated troubleshooting steps and a high level of fact orientation ensure that errors in the product or system are thoroughly investigated and thus permanently corrected instead of just solving the problem.
Application
These eight steps are performed for the 8D report:
1 Define a team to solve the problem
A team familiar with the process and/or the product is formed. They analyze the problem, take corrective actions, and monitor the effectiveness.
2 Describe the problem
In this step, the problem is defined as precisely as possible and the root cause of the problem is identified.
3 Containment action
These measures are intended to resolve the problem quickly and limit the damage until a permanent solution is found.
4 Root cause analysis
You probably haven’t found the real root cause during step 2 therefor various tests and experiments are used during step 4 to search for the real root cause of the error and the most likely causes are identified. This is intended to ensure that similar errors do not occur again.
5 Planning of counter measures
It then determines the means by which the causes of the problem can be eliminated. It is tested whether these measures solve the problem efficiently and no undesired side effects occur.
6 Check effectiveness of counter measures
Once the corrective actions have been carried out successfully, the immediate actions must be stopped. In the automotive industry, only process-improving measures are regarded as permissible shutdown measures.
7 Prevent recurrence of error
To ensure that such an error does not happen again, the team must initiate and monitor preventive measures. In the automotive and aerospace industries, manufacturers must use the FMEA method to assess the risks identified during root cause analysis. .Also, quality management system rules and procedures may need to be adjusted.
8 Appreciation of team performance and Lessons Learned
In a last step, the achievements of the team are recognized and experiences are exchanged.
Mentee
The mentee is the student of the mentor.
The mentee is the student of the mentor.
The term mentoring describes the development process in an organization where an experienced person (mentor) passes on his/her knowledge and skills on to a new/unexperienced person (mentee).
The overall aim of a mentoring program is to develop and promote the mentee’s personal and professional growth within or outside your organization.
As described the mentor refers to the role of a personal trainer whose experience supports the development of the mentee. There is also the cross-mentoring approach out there where experienced managers from different departments or companies and their high potentials (mentees) come together for tandems. Cross Mentoring usually is an externally organized program in which the tandems are formed in cross-functional and cross-industry teams.
Minimarket Principle
The minimarket is the smallest version of a supermarket on the shop floor.
The minimarket is the smallest version of a supermarket. The minimarket is typically a small area where operators can take parts from located on the shop floor. Typically C-Parts which are refilled following the Kanban/2-Bin principle. The minimarket is filled by the milkrun which pulls material from the supermarket.
Shop Floor Management
Shop Floor Management supports the consistent development of on-site processes and procedures.
Shop Floor Management (SFM) helps the constant improvement of processes and procedures on the shop floor. The presence of mgmt. level staffing in manufacturing and their recognition on deviations from requirements dramatically hastens decision-making and consequences with inside the on the spot implementation of solutions.
Shop Floor Management really defines control duties and calls for unique modes of conduct. Management is supported via way of means of the utility of unique equipment. Five Shop Floor Management-associated duties are performed on the Shop Floor and are as follows:
Install regular communication
Confirm processes
Empower/Qualify staff
Make it part of the continuous improvement process (CIP)
Conduct problem solving in a structured approach
SFM emphasizes behavior that encourages your staff to resolve issues inside their scope of capabilities and strive for continuous improvement.
For example, management maintains its remarks to a minimum, handiest makes binding commitments, offers however additionally accepts feedback, profits its personal attitude of a situation, lets in errors in mastering situations, does now no longer lay blame and places in vicinity wondering techniques. SFM tools help the effectiveness of SFMgmt. e.g.:
Production diary, KPI charts, hassle-fixing sheet, T-cards
Shopfloor Management
What is Shopfloor Management?
Shopfloor Management
Basic components of shop floor mgmt
Clear management roles and responsibilities
Regular communication (Gemba Walks)
Key Performance Indicators
Problem-solving techniques
Visualization
Some explanation of the basics of operational leadership in shop floor mgmt. you organization will for sure profit from clear leadership roles and tasks. Your employees want near help for independent problem solving. Large control gaps, wherein the direct touch among the supervisor and his personnel and associates is reduced, normally do now no longer show themselves.
The Japanese version of a classical institution leader (Hancho), with a totally small management margin and occasional willpower of the personnel, regularly does now no longer suit into the qualified operator in organizations. The excessive qualification of operators is a vital aggressive thing in industry. In order to make suitable use of those capabilities with inside the processes, disciplinary management has the mission of the use of SMART´en to acquire desires at the same time as keeping room for manoeuvre and keeping a very good stability among needs and help.
Managers at the first mgmt. level do now no longer meet those demanding situations via time control seminars, however via greater practical duties and requirement profiles. Examine whether or not it's far important to introduce extra technical management as an alleviation for the first mgmt. level to your organization (CIP coordinator, Kaizen Manager, Process Champion). This feature can stand up from the present functions.
Jointly have a look at the opportunities of dispensing distinctive information regions (5S, set-up time reduction, CIP etc.) with inside the assembly teams expand collectively with you a brand new blending answer specially appropriate for you.
Regular communication
Regular communication is the structured approach to create a framework on a regular basis for opportunities. In this rhythm issues can be carried out and discussed across the management levels. Regular communication is an integral part of the day to day work of all players in your organization.
This way of communication, no matter if you call it huddles, stand up meetings, shop floor meetings, etc. guarantees a continuous flow of information without loss of information itself as it is fast and recurring. A subject matter-associated exchange takes place where employees are enabled to independently define measures, hassle answers and pointers for development and to remedy conflicts as quick as possible.
The continuous flow of information between the departments throughout the complete organization is guaranteed through these regular and short meetings. One positive side effect is that with regular communication you will also calm down daily operations management by clearly separating the topics (e.g. operative commercial enterprise, 5S, CIP, etc.). It is vital that these regular meetings are performed continuously and adhered to in order that normal communique will become independent.
Key Performance Indicators
Regular communication can only exist if the information inside these meetings are defined and standardized. The standard of these meetings is not only the agenda but more important the Key Performance Indicators (KPI). The target of working with KPIs is to have a framework for employees that provides information on the achievement of objectives. When you want to successfully control your production be aware that KPIs are broken down in such a way that they have a direct connection to the operators or designated workstation. Only then they are becoming a real instrument of control by which teams and departments can be measured. The positive thing about KPIs is that with the continuous improvement process paired with a structured problem solving approach all employees will see the effect of implemented measures on the KPIs. To get the full information on KPIs go here.
Problem Solving
Problem solving isn’t always as simple as it sounds, but it clearly shows the effectiveness of clear shop floor management. There are plenty of problem solving methods out there (Ishikawa, 5 Why, A3, Root Cause Analysis, just to name a few) and lean methods (e.g. 5S, set-up time reduction, Hejunka etc.) are well known in the manufacturing industry. But these methods are there to help your organization to deal with more complex issues, this means that they are not really useful for operators that are dealing with daily production but more for a problem solving team consisting of employees from different departments.
To tackle problem solving the right and sustainable way the role of a Kaizen Manager should be installed in your organization in order to steer the problem solving and continuous improvement process. Kaizen Manager help you to get out of this “fire fighting mode” with a sustainable CIP culture.
Visualization
For a clear visualization of running process in your organization, cleanliness and orderliness is the main part of it. Clarity of your processes on the shop floor is the foundation for all lean manufacturing activities. Having the clarity the implementation and maintaining of visual management methods will guide you to a real state of flow.
There are different ways for visualization out there (find a deeper insight here)
The target with visual management and those methods are all the same:
Create transparency
Visual representation of procedures processes and services
Making problems (or bottlenecks) visible
All documents and information are daily updated and right at the place of action clearly visualized for everybody in the organization (e.g. blackboards, Workflow Boards, Shop Floor Boards, Andon Boards, etc.).
Following the PDCA cycle the status of problem solving activities are recorded and visualized. KPIs on different topics are installed and tracked and so on. Important is only that all this information follows also a clear structure and has its own spot on the shop floor (e.g. a shop floor corner). Visualization starts at the workplace of a operator and ends at the management board of the plant manager or owner of the organization.
But in the end it always supports the Continuous Improvement Process in order to bring your organization the next level or simply to overachieve your customers expectations. To get a full insight in Visual Management, read the full article here.
Sensei
In the lean world a sensei is a lean production expert that transfers his knowledge as mentor on to his mentees.
In the lean world a sensei is a lean production expert that transfers his knowledge as mentor on to his mentees.
To be successful with a Sensei it's been revealed that you need to start at the top and find a sensei to work with in order to engage all employees on the shop floor. As Lean activities reach industrial maturity, the role of the Sensei remains a gray area.
It is obvious that your organization needs a Sensei to adapt and successfully implement Lean principles. Therefore, the Sensei position will be your bottleneck in Lean implementation. In every Lean transformation process, one learns at some point that the success of a company consists in learning to learn.
As a little guide, consider the following three effects:
Learning curve: The learning curve of each department and initiative is tracked by their manager in the organization rather than having to compare it to established best practices across your organization.
Spillover: Effective learning practices are passed through hands-on, experiential learning from person to person within your organization rather than through predetermined processes.
Value-Based: Lean as a whole provides a learning framework that aims to balance customer satisfaction (which leads to organizational success) with employee satisfaction (and personal fulfillment) through a set of principles and tools aimed at discovering how MUDA can be reduced and value can be increased . Adding activities in all areas of the organization.
This approach has both sides of the medal, but the weak and the strength are lying in the learning path of each employee. Following the lean principles, every employee is expected to discover:
What do I need to learn: What is my personal challenge in order to better align my work with customer value and thus sustainable and profitable growth with the satisfaction of all my colleagues to reconcile.
Learning from the shop floor: The learning style is deeply embedded in daily operations. Employees are learning results from their support of learning activities at all levels. Because all employees solve their problems or show initiative, everyone is expected to interpret the conclusions of others and find a way to adopt the solutions to their own work. It is the responsibility of the Sensei to support its learners in this learning phase. Learning by doing is the correct way to describe it.
Create a learning environment for your employees: Learning on the job is never easy, especially in today's business climate. Consequently, one of the key functions of a Sensei in the Lean perspective is to create a visual environment for employees where it is easier to recognize than normal and where opportunities for continuous improvement in small steps (Kaizen in Lean jargon) are clearly visible Everyone. A learning environment also means a stable affective environment where mistakes are not punished but seen as a source of learning.
The Sensei is not a boss at all. He or She has no power and can only suggest. The Sensei's task is to help all employees in your organization to develop their own lean thinking through practical exercises in workshops. The Sensei's job is to convince middle managers that solving today's problems will, in the long run, prevent tomorrow's fires.
The essence of Lean is learning while solving problems. This is a difficult task at the best of times, and indeed every person in your organization must be taught to learn how to learn. In relation to managers, the Sensei has five main roles of support:
Finding problems
Tackling problems
Creating problems
Solving problems
And finally learnings from problems
"If you have no problems, you are dead". is a classic lean principle. Perhaps the most important part of Lean's problem-solving learning approach is the initial problem-finding phase. Lean's approach to business is to capitalize on every problem.
“Sometimes you WIN sometimes you LEARN!”
5M Method
5M Method is an other way of describing an ISHIKAWA Diagram.
5M Method is just an other way of describing an ISHIKAWA Diagram. This diagram is pre-structured with five given categories of potential causes: “Man”, “Machine”, “Material”, “Mileu = Environment” and “Methodology”. In a more detailed form of the environment you can further divide it in “management” and “measurement” which then is considered as 7M methodology.
Stay Connected
Ad
We want information fast and in a nutshell. We from OI recommend Blinkist* - because it’s simply the best.
* = Affiliate Link