LANGUAGE OF LEAN
Stay tuned - more articles coming soon!
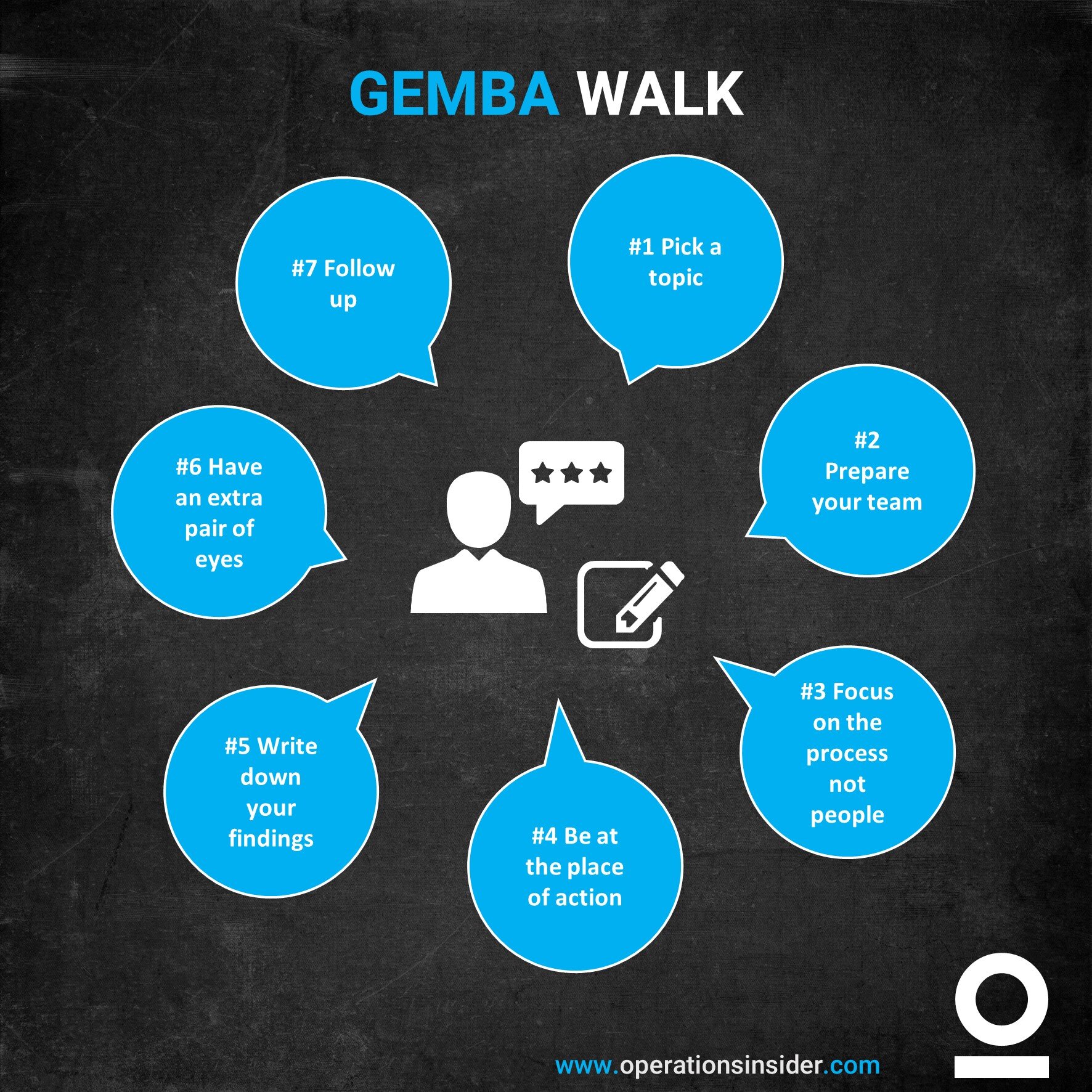
Genchi Genbutsu encourages managers and employees to leave their desks and offices and go to the place where work is being done to see firsthand how things are working.
Operational Excellence experts know the importance of establishing clear, measurable, and achievable goals in any organization.
Counter Measurements are a powerful way to track progress and identify areas for improvement, but it is important to understand the difference between short, mid, and long-term actions.
Flow is one of the key principles of Lean, and it refers to the smooth, uninterrupted progression of work from one step to the next.
The ideal state refers to a vision of a future state where processes are optimized, waste is eliminated, and efficiency is maximized.
Internal Setup, also known as Machine Changeover or Equipment Changeover, is a critical aspect of Lean Manufacturing. It refers to the process of switching a production machine from one product or production run to another.
Non-Value Adding (NVA) activities in the manufacturing industry can significantly impact the overall efficiency and profitability of a company.
We believe that MMP has the potential to bring significant benefits to a production line by increasing efficiency, reducing waste, and improving customer satisfaction.
One Point Lesson (OPL) is a method used in the manufacturing industry that can greatly improve operational efficiency and overall quality.
Order and cleanliness are two critical components of a successful and efficient work environment.
Perfection is a goal that many organizations strive for, and it is no different in the manufacturing industry.
Production smoothing, also known as Heijunka, is a key aspect of modern operations management. It refers to the leveling of production to match customer demand, while maximizing efficiency and minimizing waste.
Rapid Improvement Events, also known as Kaizen events, are a powerful tool for improving production processes in every industry.
The Product Machine Matrix is a methodology that can be used in the manufacturing industry to improve production processes and achieve operational excellence.
The 14 principles of good mgmt. described by Deming in his book "Out of the Crisis" can be seen as crucial factors for successful corporate transformation.
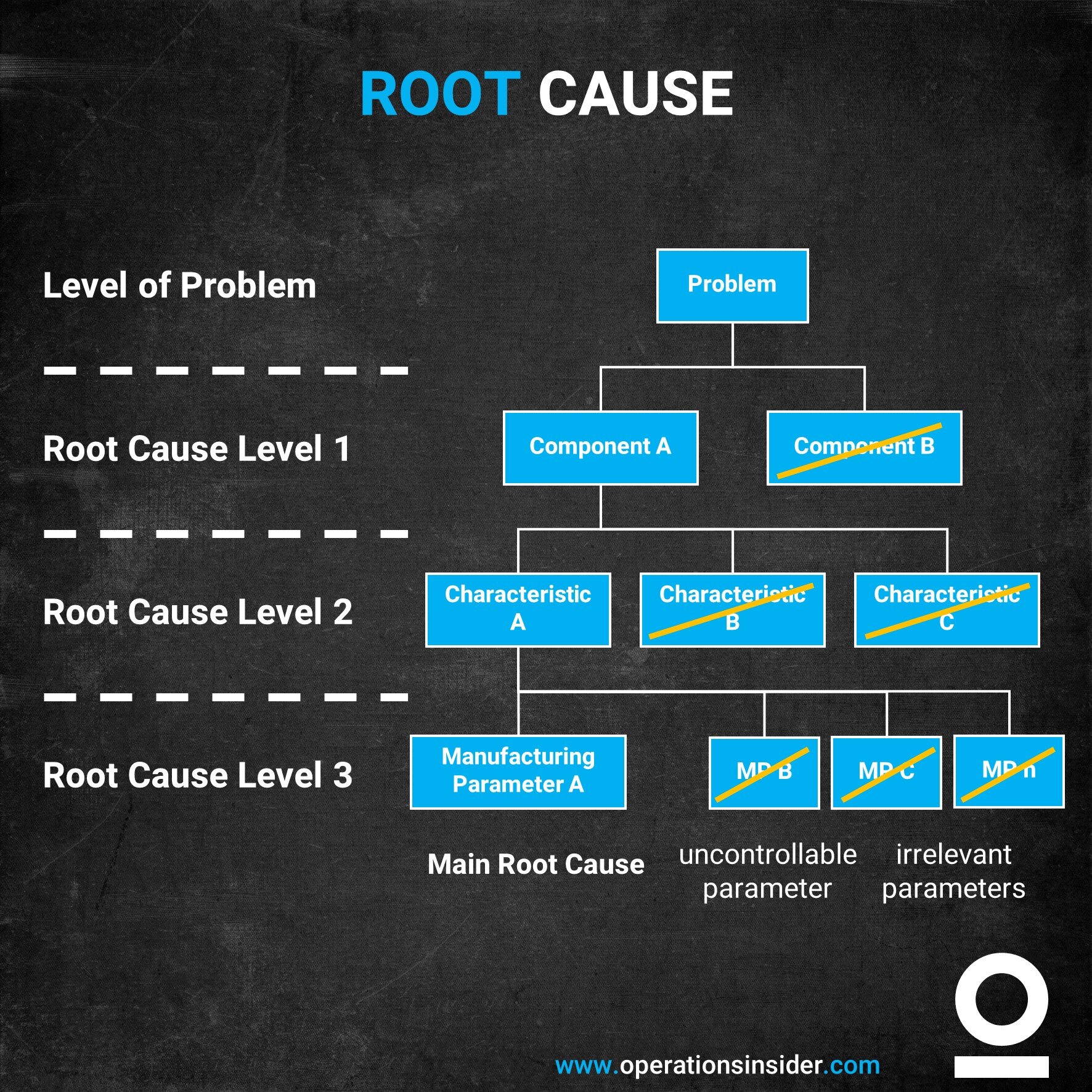
The 5 Why methodology is a well known part of the root cause analysis. Key is to ask five times in the row – why?
Point of Use (POU) is a key component of Lean initiatives aimed at reducing waste, increasing efficiency, and improving overall production processes.
One of the key principles of lean management is the flow cell principle, which is all about optimizing the flow of materials, information, and processes within a manufacturing facility.
Automated replenishment refers to the use of technology and systems to automatically manage the replenishment of materials and supplies in a manufacturing environment.
Inventory is often viewed as a necessary evil, as it provides a safety net to ensure that products are available to meet customer demand.
Standard work is a fundamental principle of Lean manufacturing, a management philosophy that focuses on the elimination of waste and the continuous improvement of processes in order to increase efficiency, quality, and customer satisfaction.
Low Cost Intelligent Automation (LCIA) has been a buzzword in the manufacturing industry for the past few years, promising to revolutionize the way companies approach production and efficiency.
ABC Analysis is a method used in the manufacturing industry to categorize inventory based on its value and usage.
Just in Sequence (JIS) is a lean manufacturing principle that emphasizes the importance of delivering components to the production line at the exact moment they are needed.
Standardization is a vital aspect of a successful lean management strategy and can be defined as the process of establishing and maintaining common procedures and processes throughout the manufacturing organization.
The bowling chart is a visual representation used in the manufacturing industry to track and monitor key performance indicators (KPIs)
Cardboard engineering, also known as corrugated cardboard engineering, is a concept that is gaining popularity in the world of manufacturing.
Line balancing is a critical component of lean manufacturing and is a key tool for improving efficiency, reducing waste, and increasing productivity.
Overproduction is one of the seven kinds of wastes in the Lean Manufacturing methodology and refers to the production of goods in excess of what is immediately required by the customer. Operations Insider - connecting the dots.
The manufacturing industry is a complex system of processes, with each stage relying on the success of the previous one to achieve the final product.
"Pacemaker" is a term commonly used in the manufacturing industry to describe a production process that sets the pace for the rest of the production line. Sometimes also considered as bottleneck station.
Building Information Modeling (BIM) is a method to optimally plan, develop and manage buildings using software.
Zero Defects, also known as "Zero Quality Control" or "ZQC," is a quality improvement philosophy that seeks to eliminate defects in the production process.
Six Sigma is a highly structured and data-driven methodology used in the manufacturing industry to improve quality and efficiency. Six Sigma offers a powerful toolset to help organizations achieve operational excellence and continuous improvement.
Regular communication refers to the continuous exchange of information between different departments and individuals within an organization.
Change overs refer to the process of switching a production line from producing one product to producing another.
Audits are a critical component of any lean manufacturing program, as they provide a structured and systematic approach for evaluating the effectiveness of the processes and procedures in place.
The use of annual objectives with 3 to 5 years breakthrough objectives is a crucial aspect of policy development in an organization.
Cell Production focuses on optimizing the flow of work and improving efficiency in manufacturing and operations.
Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) is a maintenance strategy that involves involving all employees in the maintenance process to maximize equipment productivity and minimize downtime.
Cellularization is a lean manufacturing methodology that aims to optimize the flow of materials, information, and people within a manufacturing or production environment.
MTM (Methods Time Measurement) is a systematic method for analyzing and optimizing work processes that is widely used in the field of Lean Management.
A Blue Sky Workshop is a process that is often used in organizational change management and is designed to promote creative thinking and help organizations to think beyond the boundaries of their current systems and practices.
The term "set up time" refers to the amount of time it takes to transition a manufacturing process or production line from producing one product to another.
The Hoshin Kanri Catchball Process is a key component of Hoshin Kanri methodology and is used to facilitate communication and collaboration between different levels of the organization.
Hoshin Kanri, also known as Policy Deployment, is a strategic planning and management methodology originating from Japan
The Push Principle Concept/Term refers to a production system where material and products are manufactured and moved along the production line based on a predicted demand, rather than actual demand.
The bullwhip effect is a well-known phenomenon in lean management that can have a significant impact on the push and pull principles of supply chain management.
Just-in-Time (JIT) is a manufacturing and inventory control system in which raw materials, components, and finished products are delivered to the production line exactly when they are needed.
Kaikaku first creates the basics to later carry the Kaizen idea into manual production with CIP.
KOSU, short for "Key Operating System Units", is a method used in Lean management and operational excellence to identify and measure the critical units of a process that are essential for the overall performance and success of the operation.
Machine cycle time is a term used to describe the amount of time it takes for a machine to complete one full cycle of operation.
A Swim Lane Flowchart, also known as a cross-functional flowchart, is a type of process mapping tool that is used to visually represent the flow of a process and the various roles and responsibilities involved in that process.
A standard layout is a detailed, visual representation of the ideal workflow and arrangement of resources in a given area.
A traditional general Japanese term for unevenness. It is the waste of variation in the production process.
In the world of lean, the mentor strives to improve the competencies of his / her charge and thereby improve the level of problem-solving and improvement within the organization.
The minimum amount of material or a given product, which must be in process at any time to ensure proper flow of the operation.
Muri, a Japanese term meaning "unreasonable, impossible, or overburdened," refers to the excessive demands placed on resources, such as equipment and operators, which can lead to wear and production downtime.
In lean management, a standard work combination sheet is a document that displays the process steps for one or several employees. It is used to show the optimal combination of human and machine work.
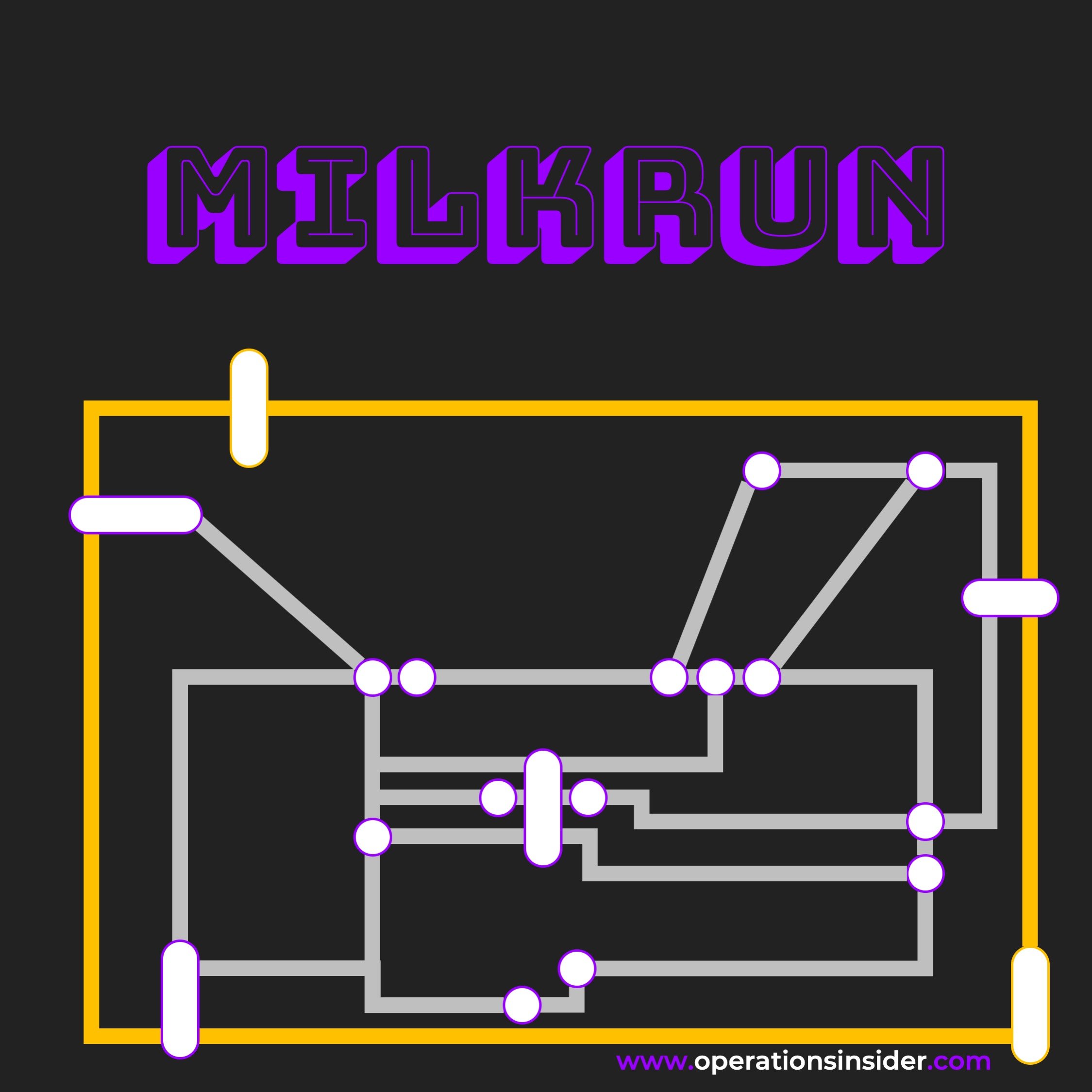
The Milkrun is the preset intralogistics concept to bring raw material, semi finished and finished goods to the place they belong at the time they are needed.
8D Reports are used to communicate results of taken problem solving steps to the customer in a standard format.
Shop Floor Management supports the consistent development of on-site processes and procedures.
In the lean world a sensei is a lean production expert that transfers his knowledge as mentor on to his mentees.
Jidoka is the Japanese word for automation. It describes a form of automation where machinery stops by itself when defects are detected and notifies humans to clarify what is going wrong.
Point Kaizen describes improvement actions concentrated on one workstation = on the spot.
In the language of Lean the term supermarket describes a ways of an independent production control.
A value stream includes all activities (value adding as well as non-value adding) in your organization that are required to deliver your product or service to the end customer.
The concept of "Quick Response Manufacturing" (QRM) describes a corporate philosophy which propagates the orientation towards the reduction of lead times as the primary goal of all corporate decisions.
Stop the line authority describes the ability or permission of operators to stop the process when problems occur. By doing so it is prevented that defective parts are passed on the downstream process steps.
The Policy Development Action Plan is a form used by the department working on Policy Development objectives.
The 14 principles of good mgmt. described by Deming in his book "Out of the Crisis" can be seen as crucial factors for successful corporate transformation.
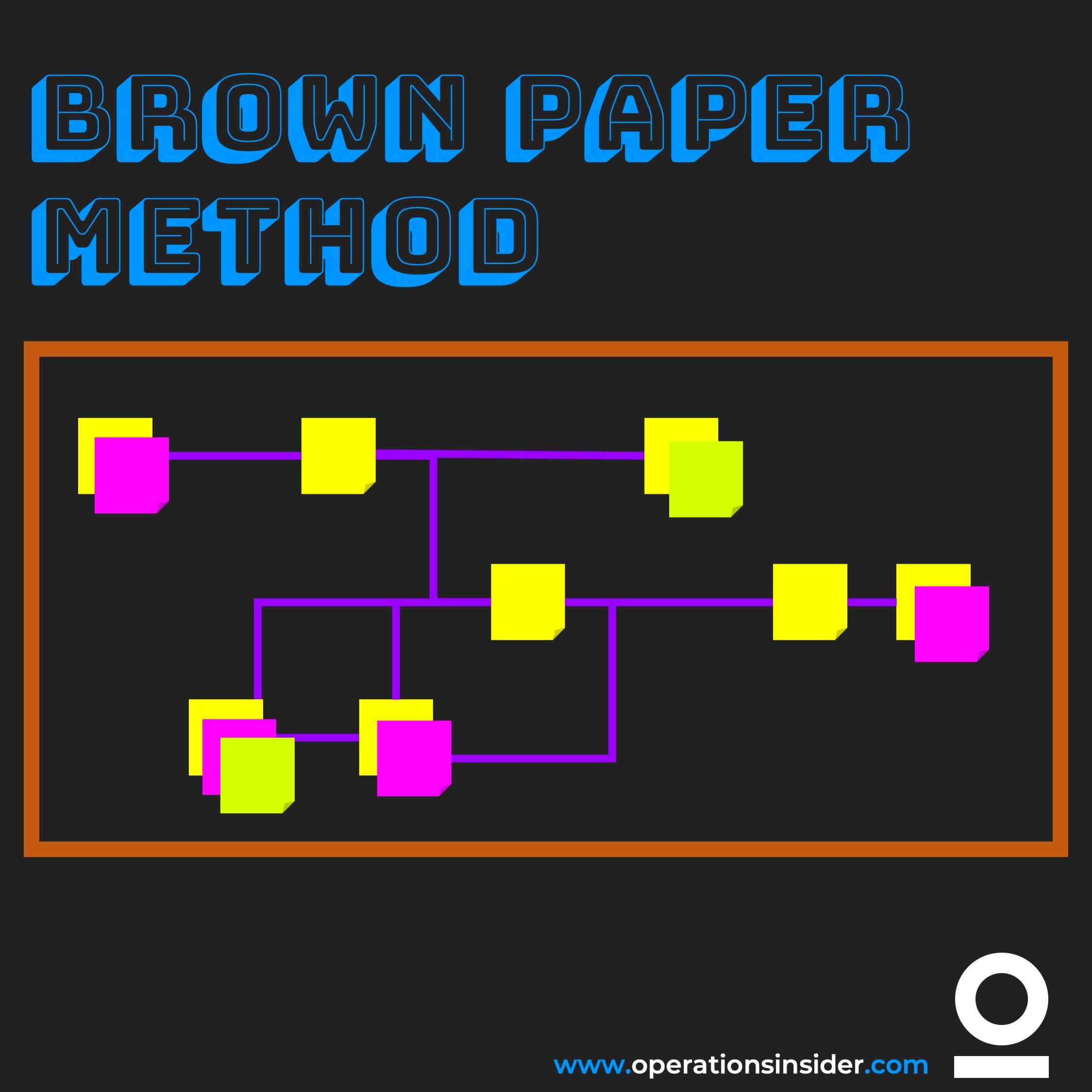
The Brown Paper Method is a practical tool to develop or improve process management in your organization.
When talking about Light House Projects this means nothing less than that a small sector of your organization e.g a department is already turned around.
The continuous improvement process is a method to continuously improve processes and procedures in companies or organizations.
"True North" - a concept that plays a key role in the journey of lean management and the road of improvements.
A Target Agreement is a management technique where employees and management together reach an agreement on how achieve the organization’s targets.
Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control. DMAIC is an incremental process improvement using Six Sigma methodology.
“Turtle Diagrams” are an effective tool to understand the processes from both a managerial and workforce perspective.
The opposite of value creating are non-value adding activities. Those can be remembered with TIMWOOD.
The 80/20 rule demonstrates that things have an unequal distribution. Out of 5 one will fly and have the most impact. With 20 percent of action 80 percent of your target state is already reached.
The method of the FMEA - Failure Mode and Effect Analysis has been used for years in the automotive and manufacturing industry.
A work place that takes into consideration most of the ergonomic aspects such as the operator’s height, range and reach.
SMART - Objectives drive us forward and continually remind us of what we want to achieve. They help us to set priorities more clearly, to focus better and give us the strength to continue, even if our motivation is low.
The idea behind the PDCA cycle is to empower employees to independently identify and solve problems. It is also a crucial element of the continuous improvement process (CIP).
The operator creating the value (doctor) receives the materials and tools from the logistics provider (nurse), so that his/her primary activity is not interrupted by secondary activities.
Constantly improving the amount of workers in a production cell to match the volume of demand and type which has been given to the unit - requires that training is provided to every worker in various process steps.
Japanese term meaning to accept your personal responsibility for your own mistakes and the will for improvement. The Hansei Assessment can be seen as deep personal reflection.
The Kamishibai Board helps your organization to visualize and manage recurring tasks in a very simple but effective way.
The 5S Method is a five-level system for the provision of safety, cleanliness and orderliness on the workplace.
Kaizen Mangers are the people in your organization who initiate changes within your organization or support departments on the path along the continuous improvement process (CIP).
The QRQC can bee seen seen as a general management attitude to solve any kind of problem at the place where it occurs.
Andon is a crucial part of visual management on the shop floor that gives a signal that indicates if and where there is a problem.
The Operator Cycle Time is the time an operator needs to fulfill a dedicated process step, including loading and unloading but excluding waiting time.
The production diary, as part of the shop floor management system, defines a shift based weekly forecast incl. upcoming tasks for mgmt., supporting functions and is openly displayed on the shop floor.
Is a device or means for automatized unload of a work item from one process or operation, providing the correct state for the next item to be loaded.
The 5 Why methodology is a well known part of the root cause analysis. Key is to ask five times in the row – why?
The affinity diagram helps you to organize a large number of ideas into logical categories and natural relations.
Single Minute Exchange of Die. A method of increasing the amount of productive time and to reduce the planned downtime to single digit minutes.
The term Kata is borrowed from Japanese martial arts and describes a series of movements following the flow of a fight.
The PPM rate (Defect Parts per Million) indicates how many NOT OK parts have occurred per million parts delivered or produced.
The Kano Model shows competitive advantage through knowledge. Therefore it shows the connection between product features and customer satisfaction.
A paradigm is a framework for thinking about something, usually a scientific or technical discipline.
Muda = waste, Muri = overload, Mura = imbalance. Read more about how to define and eliminate the 3 MUs.
6R - The right product at, the right time, at the right place, in the right quantity, in the right quality and for the right price.
A Mizusumashi is the operator responsible for supplying a workstation and keeping production going without interruption.
The U-shape layout describes the layout of machines and workstations in a one-piece-flow, where they are laid out in the shape of the letter “U”.
The term Chaku Chaku comes from the Japanese and can be translated with "load load”. Also in general it has become a term for variant of a flow or series production, and the work in it.
Read how a Hancho will support your organization as the first management level on the shop floor.
FIFO is a warehousing-related principle. The parts that were stored first are picked first.
When talking about voice of the customer (VoC) we think about the customers’ expectations which are driving product development, services and improvement of daily business..
In order-oriented production, the cycle time specifies the time from the start to the completion of the process steps.
The 5S Method is a five-level system for the provision of safety, cleanliness and orderliness on the workplace.